Wonk/Fest 2015: Exhibition and Deliverables for the Contemporary Age
This post is part 4 of an ongoing series of posts chronicling how rapid technological change is impacting the exhibition side of independent film, and how this affects filmmakers and their post-production and delivery choices. The prior three can be found at the following links: January 2013 • August 2013 • October 2014

DCPs can be proprietary hard drives. Alternatively (not shown), then can look virtually identical to external hard drives
When I started this series back in 2013, a fairly new exhibition format called DCP was starting to significantly impact independent exhibition and distribution, and I was very afraid. I was sure that the higher costs associated with production, the higher encryption threshold, and the higher cost of shipping would significantly impact the independents, and heavily favor the studios.
Flash forward to today, and of course DCP has taken over the world. And thankfully we independents are still here. Don’t get me wrong…I still kinda hate DCP…especially for the increased shipping price and their often bulky complicated cases and how they are so easily confused with other kinds of hard drives…but they are a fact of life that we can adapt to. Prices for initial DCP creation have dropped to more manageable rates in the last two years, and creating additional DCPs off the master are downright cheap. And most importantly, they don’t fail nearly as often as they used to…apparently the technology and our understanding of it has improved to the point where the DCP fail rate is relatively similar to every other format we’ve ever used.
While DCPs rule on the elite level….at all top festivals and all major theatrical chains…filmmakers still need to recognize that a wide array of other formats are being requested by venues and distributors every day. Those include BluRays, ProRes Files on Portable Hard Drives, and, most significantly, more and more requests for downloadable files from the cloud.
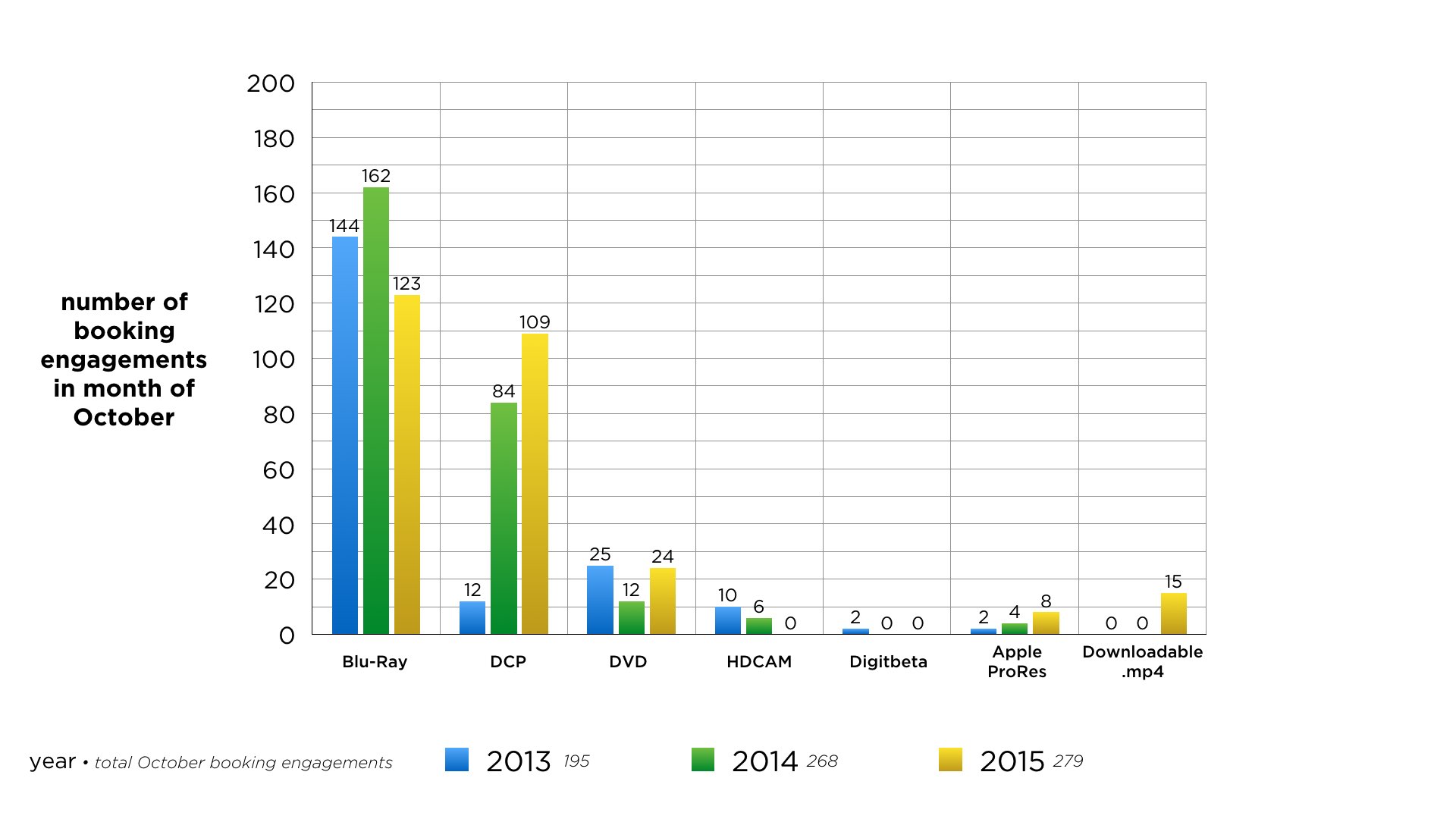
To track the evolution of formats over the last two years, please refer to the booking charts of Film Collaborative films below. Of the many things that The Film Collaborative does, one of our core services is booking our clients’ films in public venues all over the world – including everything from film festivals, traditional theatrical venues, universities, art galleries, etc. October is always the busiest month of the year…as it is the month of the year with the most film festivals. By comparing the last three Octobers, we can see quite clearly how venue deliverables have changed over the last two years.
Quick observations of the above include:
- Bluray use for exhibition has remained relatively constant over the last three years in terms of total Blurays used, although its percentage rate has declined by about 23% from last year.
- DCP use for exhibition has increased from 6.1 percent in 2013 to 31% in 2014 to 39% in 2015. It should be noted that the vast majority of high-end bookings such as top festivals or top theatrical chains require DCP now, and the vast majority of Bluray bookings are at the smaller venues.
- Digital tape formats, such as HDCAM and Digibeta, have entirely disappeared to 0. As we said in our last post to this effect….stop making these entirely!
- Requests for Quicktime files on hard drive format are on the rise…and the only reason their numbers above seem so low is because we resist booking them whenever we can—because they are an additional cost. So the 8 listed for October 2015 means in those cases we determined we had no other choice. We should discuss this further in this post.
- For the first year ever, our company is now offering downloadable vimeo links to festivals to show the film from electronic files delivered over the internet. This is a radical direction that has much to be discussed, and we shall do so later in this post. To date we are only offering these in extraordinary situations….mostly for emergency purposes.
While DCP is certainly the dominant format at major venues for now and the foreseeable future, I still maintain my caution in advising filmmakers to make them before they are needed. Nowadays, I hear filmmakers talk about making their DCP master as part of their post process, well before they actually know how their film will be received by programmers and venue bookers. Lets face it, a lot of films, even a lot of TFC member films, never play major festivals or theatrical venues, and their real life is on digital platforms. Remember that DCP is a theatrical format, so if your film is never going to have life in theatrical venues, you do not need to spend the money on a DCP.
If and when you do make your DCP(s), know that DCPs still do on occasion fail. Sometimes you send it and the drive gets inexplicably wiped in transit. Sometimes there is a problem with the ingest equipment in the venue, which you can’t control. Film festivals in particular know this the hard way….even just a year ago DCP failure was happening all the time. A lot (most) festivals got spooked, so now they ask for a DCP plus a Bluray backup. That can be a significant problem for distributors such as TFC, since it can mean multiple shipments per booking which is expensive and time-consuming. However for individual filmmakers this should be quite do-able….just make a Bluray and a DVD for each DCP and stick them in the DCP case so they travel with the drive (yes I know they will probably eventually get separated…sigh). And the Golden Rule remains….that is never ever ever travel to a festival without at least a Bluray and a DVD backup on your person. It never ceases to amaze me how many (most) filmmakers will fly to a foreign country for a big screening of their film and simply trust that their film safely arrived and has been tech checked and ready to go. If your DCP fails at a screening that you are not at…well that sucks but you’ll live. If you travel to present your film at a festival and you are standing in a crowded theater and your film doesn’t play and everyone has to go home disappointed, that, in fact, is a disaster.
As mentioned previously, more and more venues that cannot afford to upgrade to DCP projection are choosing to ask for films to be delivered as an Apple ProRes 422 HQ on a hard drive. Since this is not a traditional exhibition format, a lot of filmmakers do not think they need to have this ready and are caught unawares when a venue cannot or will not accept anything else. At The Film Collaborative, we keep a hard drive of each of our films ready to go at our lab…as mentioned we do not prefer to use them because of the extra shipping cost (DCPs are trafficked from festival to festival so at no shipping cost to us, while hard drives are not used often enough to keep them moving like this). However we do find we often need them in a pinch. So do keep one handy and ready to go out. This should not be a big deal for filmmakers, since the Apple ProRes 422 HQ spec is the most important format you’ll need for nearly all types of distribution deliveries, whether it be to distributors or digital aggregators or direct to digital platforms. So, if you plan to have any kind of distribution at all, this is a format you are almost certainly going to need. Make a couple to be safe.
Is the Future in the Cloud?
As I have touched on before, the Holy Grail of independent film distribution would seem to live in the cloud, wherein we could leave physical distribution formats behind and simply make our films available electronically via the internet anywhere in the world. This would change the economics of independent film radically, if we could take the P out of Prints & Advertising and save dramatically on both format creation and format shipping. Unfortunately today’s reality is far more complicated, and is not certain to change any time soon.
I can’t begin to tell you how often…nearly every day…small festivals looking to save on time and shipping will ask me if I can send them the film via Dropbox or WeTransfer or the like. The simple answer is no, not really. So every time they ask me, I ask them back…exactly how do you think I can do that? What spec do you need? What is the exact way you think this can work? And they invariably answer back…“We don’t know…we just hoped you’d be able to.” It is utterly maddening.
Here’s the tech-heavy problem. Anyone can get a professional-sized Dropbox these days…ours is over 5,100 gigs (short for Gigabytes, or GB) and an average 90 minute Apple ProRes 422 HQ is around 150 gigs…so that doesn’t seem like a problem. Clearly our Dropbox can fit multiple films.
The current problem is in the upload/download speed. At current upload speeds, a Apple ProRes 422 HQ is going to take several days to upload, with the computer processing the upload uninterrupted all the time (running day and night). Even this upload time doesn’t seem too daunting, after all you could just upload a film once and then it would be available to download by sending your Dropbox info. However, the real problem is the download…that will also take more than a day on the download side (running day and night) and I have yet to ever come across a festival or venue even close to sophisticated enough to handle this. Not even close. Think of the computing power at current speeds that one would need to handle the many films at each festival that this would require. And to be clear, I am told that WeTransfer is even slower.
To make this (hopefully) a little clearer…I would point out four major specs that one might consider for digital delivery for exhibition.
- Uncompressed Quicktime File (90 mins). This would be approx. 500 gigs. Given the upload/download math I’ve given you above, you can see why 500 gigs is a non-starter.
- Apple ProRes 422 HQ (90 mins). Approx 150 gigs. Problematic uploaded/download math given above. Doesn’t seem currently viable with today’s technology.
- HD Vimeo File made available to download (90 mins). Approx 1.5 – 3 gigs. This format is entirely doable—and we now make all our films available this way if needed. This format looks essentially the same as Bluray on an HD TV, but not as good when projected onto a large screen. This can be instantaneously emailed to venues and they can quickly download and play from a laptop or thumb-drive or even make a disc-based format relatively inexpensively. However, there are two major problems…a) most professional venues that value excellent presentation values and have large screens find this to be sub-par projection quality and b) this is a file that is incredibly easy to pirate and make available online. For these reasons, we currently use these only for emergency purposes…when we get last minute word that a package hasn’t arrived or an exhibition format has failed. It is quite a shame…because this is incredibly easy to do, so if we could find the right balance of quality and security…we would be on this in a heart-beat.
- Blu-Ray-Quality File (Made available via Dropbox)(90 mins). This spec would be just around the same quality as a Bluray (which is quality-wise good enough for nearly all venues) and made available via Dropbox or the like. It is estimated that this file would be around 22 – 25 gigs. This would be slow, but potentially doable according to our current upload/download calculations. This is the spec we at TFC are currently looking at…but to be clear we have NOT ever done this yet. Right now it is our pipe dream…and our plan to implement in 2016. I will follow up on this in further posts!
To conclude, where we stand now, we have yet to find a spec that is reasonably made available to venues via the internet, both in terms of quality and safety protocols…but a girl can dream.
It is critical to note that the folks I am talking to recently are saying this may NOT change in the foreseeable future…because internet speeds worldwide might need to quintuple (or so) in speed to make this a more feasible proposition. Nobody that I know is necessarily projecting this right now. And that’s a sobering prospect that might leave us with physical deliverables for quite a while now. And for now, that would be the DCP with Bluray back-up. If this changes, you can be sure we will write about it here.
But hey, maybe that Quantum Computer I’ve heard about will sudden manifest itself? Gosh, that would be cool. In the meantime…how about a long-range battery that runs an affordable electric car and is easy to recharge? That would be super cool too. We can save the world and independent film at the same time.
In the meantime…if you think I am missing the point on any of the nerdy details included in this post, or you know anything about how digital delivery of exhibition materials that I might have missed, please email me. Trust me….we want to hear from you!
Jeffrey Winter November 24th, 2015
Posted In: Digital Distribution, Distribution, Film Festivals, Theatrical, Uncategorized
Tags: Apple Pro-res, BluRay, DCP, Digital Cinema Package, digital film delivery, DVD, film deliverables, film distribution, film exhibition, HDCam, Jeffrey Winter, Prints and Advertising, The Film Collaborative
Top 5 Errors Filmmakers make when doing DIY Distribution to iTunes and other Platforms

Always check with your lab or distributor to make sure their deliverable specs adhere to what is outlined below. Especially deliverables outside North America, which are sure to diverge from what is below. Much of this may apply to films who have sold to distributors, but this post is mostly aimed at those doing DIY distribution. The following also mostly applies to TVOD platforms, but may also apply to others. Again, check with your distributor/lab before you produce any deliverables.
- Know when not to do iTunes
iTunes is expensive. It will cost at least $2K to do iTunes/Amazon/GooglePlay. Think of how many people will need to rent your film at $4 (and that’s before the platform’s cut) for you to recoup that money, and then think how many more will have to do so for you to recoup your investment. Are your 1500 Facebook fans going to come through for you? Most probably won’t. A better option might be to do VHX or Vimeo on Demand and spend that money on marketing to drive people to your site. We have handled almost 50 films in the past three years via our DIY Digital Distribution Program, and the bottom line is that if you expecing people to find your film simply because it’s on iTunes while you sit back and move on to your next project, you are probably going to be in for a rude awakening. - Subtitles and Closed Captioning (part 1)
Pretty much the only way to go nowadays is to submit a textless master, with external subtitles. This can get kind of tricky, so it’s important to understand what is needed and to not expect that the lab you are working with is impervious to mistakes.- Your film is in English and has no subtitles
You will need to produce a Closed Captioning file - Your film is 100% not in English
You will need to produce a subtitle file only (Closed Captioning is not required) - Your film is mostly in English but there are a few lines (or more) of dialogue that are not in English
You will need to produce both a Closed Captioning file and what is called a Forced Narrative Subtitle file.
This “Forced Narrative” subtitle file is rather a new concept, so when you work with your subtitle lab (if you need suggestions for labs to work with, check out the ‘Subtitling, Closed Captioning and Transcription Services and Solutions’ section on the ResourcePlace tab on our website), make sure they understand that an English language forced narrative file (unlike Closed Captioning or regular subtitles) does not need to be manually turned on for territories where English is the main language, and in fact cannot be turned off in those Territories. Hence, they are forced on the screen. Together with the closed captioning, they make up a complete dialogue of your film, but they should not overlap, or else you’ll be in a situation where the same lines of text are appearing twice on the screen, and your film will be rejected.
TECH TIP: We recommend watcing your film through before you deliver with all subtitle and CC files. If your film is only in English and you only need to produce closed captioning, these files are pretty much gibberish. So ask the lab to ALSO provide you with a .srt subtitle file of the closed captioning (it’s an easy convert for them). Even though you won’t be submitting this file, you can watch it using, for example, VLC. Just make the filename of your .srt file the same as your .mov or .mp4 file, place it in the same folder, and the subs should automatically come on.
If your film has a forced narrative, keep track of your non-English dialogue…easy to do especially if your film only has a few lines of non-English. Then change the file extension .srt or .stl temporaily to .txt. This file can then be opened in any text application and eyeballed to ensure that no lines of foreign dialogue are misplaced. If you ask for a .srt conversion of your Closed Captioning file, you can do the same thing with this file to verify that these non-English lines are not repeated in the Closed Captioning. - Your film is in English and has no subtitles
- Subtitles and Closed Captioning (part 2)
Closed Captioning needs to be in .scc format. Subtitles need to be in either .srt or .stl format. But .srt file do not hold placement, so if you are making a documentary, for example, you will probably want to submit .stl. Because if you have any lower-thirds in your film, lines of closed captioning or subtitled dialogue needs to be moved to the top of the screen when lower thirds are on the screen. .srt files will appear on top of the lower thirds, and your film will be rejected.
TECH TIP: Again, watch your film back with closed captioning / subtitling to make sure your lower thirds are not blocked. - Dual Mono not allowed
Make sure the audio in your feature and trailer is stereo. This does not merely mean that there is sound coming out the L & R speakers. It means that these two tracks need to be different…and not where one side gets all the dialogue and the other gets the M&E. Think of how annoying that would be if you were in a theater. L & R tracks need to be mixed properly and outputted as such.
TECH TIP: Listen to your film before you submit, or at the very least make sure your film is not dual mono…download an applcation such as Audacity, a free program, and open your masters in that program. if the sound waves are identical for both L & R, you need to go back and redo. Don’t assume your sound guy is not infallable. - 720p not allowed
iTunes is no longer accepting 1280×720 films. In addition, they will not take a 1280×720 that has been up-rezed to 1920×1080. No one should be making movies in 720p and expect the world to cater to their film.
David Averbach September 16th, 2015
Posted In: Amazon VOD & CreateSpace, Digital Distribution, Distribution Platforms, iTunes, Vimeo
Tags: Amazon, audio on your film file, closed captioning for film file, David Averbach, Digital Distribution, filmmaker mistakes, Google Play, HD for film file, independent film, indie film, iTunes, subtitling, The Film Collaborative, TVOD, VUDU, YouTube
The Face-to-Face Teaching Exemption and Fair Use in Education Distribution: Clearing up some misconceptions
Written by Orly Ravid and Guest co-Author Jessica Rosner, who has been a booker in the educational, nontheatrical and theatrical markets since the days of 16mm. Recent projects include Jafar Panahi’s This Is Not a Film and John Boorman’s Queen and Country.
 A recent blog by Orly Ravid covered just a little bit about educational rights and distribution. This blog is intended to develop that in response to a comment about the “Face-to-Face” teaching exception. This exception defines what films can be shown for no license or permission by the producers or rights holders.
A recent blog by Orly Ravid covered just a little bit about educational rights and distribution. This blog is intended to develop that in response to a comment about the “Face-to-Face” teaching exception. This exception defines what films can be shown for no license or permission by the producers or rights holders.
The Copyright Act provides for an exception to needing a copyright holder’s permission to exhibit a copyrighted such as a film. That exception, however, is only for “face-to-face teaching” activities of a nonprofit educational institution, in a classroom. That’s why it’s called the “face-to-face” exemption.
I emphasized the key words to clarify that this exception does NOT apply to social club or recreational screenings of films or any exhibition that is not in “classroom” or “similar space devoted to instruction” where there is face-to-face instruction between teacher and student and where the exhibition relates to the educational instruction. Second, not all institutions or places of learning are non-profits. All this to say, the “face-to-face” exemption is not a carte blanche free-for-all to show any copyrighted work in any context as long as there are books around within a mile radius. This is important because educators and distributors are often unclear about what can and cannot be done under this exception to proper permission to distribute or exhibit a film without permission (which often includes a fee).
Below is some key information about the state of educational distribution in 2015 and can be done lawfully without the licensor’s permission (under the Copyright Act):
Viable options for educational distribution that involves either selling physical copies, download, or licensing streaming rights or other rights and type of rights or sales, including price points, terms, limitations, etc.
It’s important to understand that “educational sales & use” is not legal term and that educational institutions have the right to purchase any film that is available from a lawful source and use it in an actual physical class under the “face-to-face” teaching section of copyright law (discussed above). Also okay is for them to keep a copy in the library and circulate as they choose.
However, if as increasingly the case, they wish to make films available via streaming or to exhibit them outside of a class they must purchase those rights. A filmmaker or distributor can charge a higher price to an institution to purchase a DVD if they control all sales but that would be a contract situation and mean the film basically has no sales to individuals. This is done but mostly with non-feature films or ones whose market is intended to be only institutions and libraries.
Streaming rights offer a real opportunity for income for filmmaker provided they are willing to sell rights to institutions in “perpetuity” (meaning, forever). They will make more money and the institution is far more willing to purchase. Many if not most universities now want to have streaming rights on films that are going to be used in classes.
Exhibition of film at universities or educational institutions that is NOT paid for (not licensed or bought from copyright holder) – when is it legitimate (lawful) and when is it not so?
It is legal to show the film in the classroom provided it is legal copy (not duped, bought from pirate site, or taped off television). Any public showings outside the classroom are illegal. Streaming entire feature films is also illegal but streaming clips of films is not.
What is the reason or rationale for the non-lawful use?
If it is a public showing (exhibition) they (and this is usually either a student group or professor, not administration) claim “they are not charging admission” and/or that “it being on a campus” makes it “educational and in extreme cases they claim that it actually IS a class. Illegal streaming is far more insidious and involves everything from claiming streaming a 2-hour film is “fair use,” (which would justify showing it without permission) or, that somehow a dorm room or the local Starbucks is really a classroom. Bottom line: not all use of film can be defended as “fair use.” Exhibiting not just clips but a whole film is usually not lawful unless the “face-to-face” teaching exemption requirements (discussed above) are met.
There is a disconnect for these educational institutions between how they treat literature vs. cinema:
All the parties involved in streaming (legal and illegal) librarians, instructors, tech people, administrators know that if they scanned an entire copyrighted book and posted on campus system for students to access it would be illegal but some of the same people claim it is “fair use” to do with a film. I actually point blank asked one of the leading proponents of this at the annual American Library Association Conference if it was legal to stream CITIZEN KANE without getting permission or license and he said yes it was “fair use” when I followed up and asked if a school could scan and post CATCHER IN THE RYE for a class he replied “that is an interesting question.” It is important to note that “fair use” has never been accepted as a justification for using an entire unaltered work of any significant length and recent cases involving printed material and universities state unequivocally that streaming an entire copyrighted book was illegal.
Remedies to unlawful exhibition of copyrighted works for distributors or licensors:
Independent filmmakers need to make their voices heard. When Ambrose Media a small educational company found out that UCLA was streaming their collection of BBC Shakespeare plays and took UCLA to court supported by many, other educational film companies, academics reacted with fury and threatened to boycott those companies (sadly the case was dismissed on technical grounds involving standing & sovereign immunity and to this day UCLA is steaming films including many independent ones without payment to filmmakers). For decades the educational community were strong supporters of independent films but financial pressures and changing technology have made this less so. (Jessica Rosner’s personal suggestion is that when instructors protest that they should not have to pay to stream a film for a class, they should be told that their class will be filmed and next year that will be streamed so their services will no longer be needed). Orly Ravid gives this a ‘thumbs up’.
Of course remedies in the courts are costly and even policing any of this is burdensome and difficult. Some films have so much educational distribution potential that a distribution plan that at first only makes a more costly copy of the film/work available would prevent any unauthorized use of a less expensive copy or getting a screener for free etc. But not all films have a big enough educational market potential that merits putting everything else on hold. And once the DVD or digital copies are out there, the use of that home entertainment copy in a more public / group audience setting arises. As discussed above, sometimes it’s lawful, and sometimes, it’s not but rationalized anyway. It is NEVER legal to show a film to a public group without rights holder’s permission. Another viable option for certain works, for example documentaries, is to offer an enhanced educational copy that comes with commentary, extra content, or just offer the filmmaker or subject to speak as a companion piece to the exhibition. This is added value that inspires purchase. Some documentary filmmakers succeed this way. It is extremely important to make sure your films are available for streaming at a reasonable price.
Parting thoughts about educational distribution and revenue:
Overall, we believe most schools do want to do the right thing but they are often stymied when they either can’t find the rights or they are not available so get the word out.
Streaming rights should be a good source of income for independent filmmakers but they need to get actively involved in challenging illegal streaming while at the same time making sure that their works are easily available at a reasonable price. It can range from $100 to allow a school to stream a film for a semester to $500 to stream in “perpetuity” (forever) (all schools use password protected systems and no downloading is allowed). TFC rents films for a range of prices but often for $300. You may choose to vary prices by the size of the institution but this can get messy. Be flexible and work with a school on their specific needs and draw up an agreement that protects your rights without being too burdensome.
Happy distribution!
Orly & Jessica
Orly Ravid August 20th, 2015
Posted In: Distribution, education, Legal
Tags: educational distribution for films, fair use, film exhibition, film streaming rights, independent film, Jessica Rosner, Orly Ravid, The Film Collaborative
Letter to Filmmakers of the World: What Do You Want Next?
Dear Filmmakers of the World,
I write to you to ask: what do you need, what do you want?
For five years The Film Collaborative has been excelling in the film festival distribution arena and education of filmmakers about distribution generally and specifically as to options and deals. TFC also handles some digital distribution directly and through partners. And we have done sales though more on a boutique level and occasionally with partners there too, though never for an extra commission. You know how we hate extra middlemen! We even do theatrical, making more out of a dollar in “P&A” than anyone and we do a really nice job TFC has a fantastic fiscal sponsorship program giving the best rates out there.
TFC published two books in the Selling Your Film Without Selling Your Soul series and we are probably due to write a third, detailing more contemporary distribution case-studies. I got a law degree and am committed to providing affordable legal services to filmmakers and artists, which I’ve started doing.
We have never taken filmmakers rights and find that most filmmakers are honorable and do not take advantage of that. We trust our community of filmmakers and only occasionally get burned. And we have accounted without fail and paid every dollar due. No one has ever said otherwise. We do what we say we’re going to do and I am so proud of that and so proud of the films we work with and the filmmakers in our community.
So, now what? What do you, filmmakers of the world, want more of? What don’t you need anymore?
Personally, I find it staggering and sad how much information is still hidden and not widely known and how many fundamental mistakes are made all the time. Yet, on the other hand, more information is out there than ever before and for those who take the time to find and process it, they should be in good shape. But it’s hard keeping up and connecting-the-dots. It’s also hard knowing whom to trust.
TFC continues to grow and improve on what it excels at, e.g. especially festival/non-theatrical distribution. We’ve got big growth plans in that space already. My question to you is, do you want us to do more Theatrical? Digital? Sales? All of it? More books? What on the legal side? Please let us know. Send us an email, tweet, Facebook comment, a photo that captures your thought on Instagram, or a GoT raven. I don’t care how the message comes but please send it. We want to know. TFC will listen and it will follow the filmmakers’ call.
We’re delighted to have been of service for these last 5 years and look forward to many more. The best is yet to come.
Very truly yours,
Orly Ravid, Founder
p.s. our next new content-blog is coming soon and will cover educational distribution and copyright issues.
Orly Ravid July 29th, 2015
Posted In: Distribution, education, Film Festivals
Tags: film distribution, film festival distribution, Film Festivals, independent filmmakers, Selling Your Film Outside the U.S., Selling Your Film Without Selling Your Soul, The Film Collaborative
Thoughts on the EU Digital Single Market
Some of you may have heard that about a week ago the European Film Commission announced the Digital Single Market Plan (which may also apply to TV licensing). Variety covered the story HERE and HERE.
You can read for yourself what the fuss is all about but essentially, the EU Film Commission’s plan is to combine the 28 European territories into a common market for digital goods, which would eliminate “geo-blocking,” which currently bars viewers from accessing content across borders – and yet purportedly, the plan would preserve the territory by territory sales model. Filmmakers, distributors, the guilds, et al argue that this proposal would only help global players / platforms such Netflix, Amazon and Google, which would benefit from a simpler way to distribute content across Europe.
The IFTA (International Film and Television Alliance) expressed concerns that this would enable only a few multinational companies to control film/tv financing. Variety noted that although politicians insist the idea of multi-territory licenses won’t be part of the plan, those in the content industry remain concerned about passive sales and portability and the impact on windows and marketing.
In the US, digital distribution is just hitting its stride and is also finally getting anchored properly in Europe. Now this idea would be one step closer to one-stop-digital shopping, or selling. Though allegedly that’s not in the plan – but it would sure be a step in that direction.

photo credit: movantia
Some are railing against it and warning against eliminating territory sales and windowing, hurting financing, and truncating important local marketing. Well, maybe and maybe not. I think it depends on the type of film or film industry player involved. A blockbuster studio hit or indie wide release sensation with international appeal may very likely be big enough to sell many territories, be big enough to warrant spending significant marketing money in each territory’s release, and be culturally malleable enough to lend itself to new marketing vision, materials, and strategies per market. On a related note, I remember hits such as Clueless being translated into different languages not just literally, but also culturally – modified for local appeal. That’s great, and possible, for some films.
But for most of the films we distribute at TFC and for the great majority on the festival circuit, they’ll be lucky to sell even 10 territories and many won’t sell even half that. Some sales in Europe are no minimum guarantee or a tiny minimum guarantee, just like it is State-side. Some films are financed per EU territory (government funding often) but that’s on the decline too.
The dilemma here about a digital single market in the EU recalls another common dilemma about whether to hold out for a worldwide Netflix sale or try to sell European TV or just EU period, one territory at a time. I’m not forgetting Asia or Africa but focusing on the more regular sales for American art house (not that selling Europe is an easy task for most American indies in any case). Sure, if you can sell the main Western European countries and a few Eastern ones that’s worthwhile taking into account. However, so often one does not sell those territories, or if one does, it’s for a pittance. Some sales can be for less than 5,000 Euros, or half that, or zero up front and not much more later. It’s not like the release then is career building either or a loss leader. It’s just buried or a drop in a big bucket.
In cases such as these, it makes little sense to hold off for a day that never comes or a day that really won’t do much for you. All this to say, I don’t think this proposal is one-size-fits all but I do think it’s worth trying on especially if you are in the petite section of the cinema aisle. If you are not sure how you measure up, ask around, comparison shop – see what films like yours (genre, style, topic, cast, festival premiere, budget, other names involved and other aspects) have done lately. Sometimes a worldwide Netflix deal may be the best thing that ever happened and I reckon that similarly, sometimes a plug and play EU digital deal (if this vision comes into fruition) will give you all that you could get in terms of accessing European audiences, while saving you money (in delivery and fees etc.). And then, get this, you can focus on direct-to-audience marketing – something few agents or distributors do much of anyway.
I kept this blog entry short as I stand by for more information out of Cannes and beyond and also await our TFC resident EU digital distribution guru Wendy Bernfeld (Advisory Board Member and co-author of the Selling Your Film Outside the U.S. case study book) to weigh in. In the meantime, I think it would be swell if one Cannes do digital in the EU all at once.
Please email me your thoughts to contactus [at] thefilmcollaborative.org or post them on our Facebook page so we can update this blog. We turned off comments here only because of the amount of spam we received in the past.
Orly Ravid May 14th, 2015
Posted In: Digital Distribution, Distribution
Tags: Amazon, arthouse films, digital film distribution, Digital Single Market Plan, EU, Film commission, Google, independent film, International Film and Television Alliance, Netflix, Orly Ravid, Selling Your Film Outside the US, The Film Collaborative, Variety, Wendy Bernfeld
TFC’s Film Distribution Takeaways of 2014
As 2014 draws to a close TFC reflects on five (5) film distribution lessons from 2014 in anticipation of our 5th Anniversary at Sundance 2015.
1) DIGITAL TECHNOLOGY POSITIVELY IMPACTING FESTIVAL & OTHER PUBLIC EXHIBITION DISTRIBUTION BY REDUCING COST AND HEADACHE:
As we have seen every year for several years now, we are experiencing additional technological revolution that will change our business forever. In 2014, we said adieu to the preview DVD (for festivals, distributors, exhibitors, press etc.) in favor of the online screener link. We said goodbye to the HDCAM and the final nail in the coffin of the Digibeta. We struggled with the problems of the DCP and all its imperfections and inevitability (at least for a few more years). And we are RIGHT ON THE VERGE of the greatest evolution we will experience in recent years, which will be full delivery of films for exhibition via the Internet…whether it turns out to be Vimeo or Drop Box or iCloud or other. If we can remove the SHIPPING part of the independent film business, filmmaker (and distributor) profits may greatly increase without that part of the equation. We are almost there now…
2) THE HARD-TO-ACCEPT REALITY OF MARKETING SMALL FILMS:
As much as all of us at TFC have talked about the need to identify and target niche audiences, the ones who would be the most interested and excited to see a project because it speaks to a belief or lifestyle or cause, most indie filmmakers still aren’t heeding this advice. Of the consultations I had this year, most were with filmmakers who made micro-budget dramas with no notable names and were without prestigious festival accolades. They still believed a distributor would be willing to take on their project and give it a full release. Even those who realized this wasn’t going to happen found the financial burden associated with the kind of release they envisioned too difficult to bear, especially because they were likely to never see that money again (hence why distributors weren’t willing to take on the burden).
If you’re going to work small, you need to think small, but deep. You NEED a small, but highly passionate audience that you can reach given the resources and assets you have. Their enthusiasm will help you if you can harness their attention early on. I won’t say this is easy, but before you embark on a project that could take thousands of dollars and years of your life, first think about how you will approach the audience for your work and how you will maintain it on a consistent basis. If you think someone else is going to take care of that for you, you haven’t been paying attention to the shifts in the indie film marketplace.
If you think someone else is going to [attract and maintain a niche audience] for you, you haven’t been paying attention to the shifts in the indie film marketplace.
3) WHEN BROADCASTERS WANT STREAMING RIGHTS – WHAT TO DO?:
Increasingly, broadcasters are seeking streaming rights along with traditional TV broadcast rights and they have holdbacks on streaming and SVOD at a minimum, and often on transactional digital (DTO/DTR) too. For sure they limit / prohibit cable VOD. As a filmmaker, you only have leverage to demand a higher licensing fee if your film is a hot commodity. Otherwise, while online (or in-app) streaming will possibly gut your transactional VOD sales, you can’t beat the reach a broadcaster can give to your film. Think very hard about turning down a broadcast deal that includes online streaming. Will your iTunes/Amazon/Google Play sales really be so much if very few people have heard of your film? iTunes and Amazon are not going to promote your film like a broadcaster would.
Then again, which broadcaster is it? How big is its reach? How much publicity and marketing will you get? How much digital distribution are you barred from and for how long? Not all types of films make the same money on all types of platforms so does your film demand-to-be-owned? or is a renter, at best. Not all platforms will even accept all films (e.g. all Cable VOD, Sony Playstation, Netflix). Is yours one that will digitally succeed broadly or narrowly, or at all? Will Netflix pay 6-figures like in the good ole days or a lot less, or anything? Do you have a direct-to-fan distribution strategy that you can employ in tandem so as to not need to rely on other digital platforms in the first place?
Or if you want to try it all, still, your strategy would privilege the direct sales anyway. Which is better for your goals, a film that gets national broadcast airings or a film that turns down that opportunity only to be buried in the iTunes store? Or would it not be buried? Only you can answer this as not everyone’s goals are the same and not everyone’s opportunities / potentials are the same. As we have always said, knowing your film’s ACTUAL potential and combining that with your HIERARCHY OF GOALS will help you answer these questions and decide your distribution strategy.
And while it may feel like you are giving up revenue by allowing your film to be streamed (hopefully for a limited time!) through a broadcaster’s portal, you may find this is a good career move for your next feature because people will be familiar with your work having had the opportunity to see it.
4) THE HEAVY BURDEN OF THE NARRATIVE WITH NO NAMES:
Several of us opined about the challenges facing narratives with no names.
The emerging mega strength of incredible television series available everywhere threatens narrative film even more than before, and of course, especially the smaller indie fare.
We have seen time and again how narrative dramas or comedies almost always fall flat in sales unless they have very strong names and not just C-list or B-list names. Of course there are exceptions to this rule and Sundance can be part of that, or a hot director, or simply just an exceptional break out film. But too many filmmakers look to those as the model when they are the anomaly. The pattern we, at TFC, see repeated too often is the making of a decent or good but not exceptional narrative with names that are okay but not great and then wasting time trying to make a big or even medium sale. It just does not happen. Money and time are lost and careers often not made. Again, there are exceptions, and of course certain niches such as LGBT may be one of them, but we advise discerning between passionate optimism and sheer folly.
5) TRANSPARENCY—The Kale of Film Distribution:
The big takeaway from 2014 about TRANSPARENCY is that, on the one hand, it has become a sort of new, hip standard—something cool and good, like eating kale—that more honest distributors practice and/or shadier ones pretend to because it’s more expected. On the other hand, however, we were surprised at how many filmmakers still resist it—resist sharing their data, even anonymously. And to that, all we can ask is, what are you afraid of? It’s meant to be good for the filmmaking community as a whole but maybe individually folks are scared about what the truth will bring. And some folks just want to eat bacon. We get it. Still, we encourage sharing the real data for the greater good and we will keep on working to inspire and facilitate more TRANSPARENCY.
We at TFC wish you and yours a delightful new year and we are looking forward to being even more of service to filmmakers in 2015!
Orly Ravid December 29th, 2014
Posted In: Digital Distribution, Distribution, DIY, Marketing, Uncategorized
Tags: audience building for films, broadcasters, DCP, direct-to-fan film distribution, distribution strategy, DVD, film distribution, film exhibition, Film Festivals, independent film distribution, independent film with no names, The Film Collaborative, Vimeo
Battle for festival supremacy-TIFF vs Sundance
A knockout victory
The Toronto International Film Festival (TIFF) is just behind us and films submitted for Sundance are a month away from their acceptance call. While the difference between Toronto/Sundance and SXSW/Tribeca is pretty clear, what separates Toronto from Sundance might surprise you.
I looked at the data from the last two year’s of each festival and came up with one big conclusion. Sundance is the bigger festival for North American distribution on just about every measurable level I could come up with.
How could this be? Toronto is the more mainstream fest, right? Not so much.
Let’s start with some comparative info that would clearly skew things in Toronto’s favor:
-62.5% of films from TIFF 2013 have US distribution
-81.3% of films from SUNDANCE 2014 have US distribution (and remember this was accomplished in 9 months compared to TIFF’s 13 months)
But what about the box office performance?
Sundance has a higher percentage of films that grossed over $1 Million, $500,000, and $100,000 than TIFF. This is including non world premiere films which would give TIFF an advantage.
But what about the size of the deals? Isn’t TIFF where the big money is? Hardly
11 films from TIFF 2014 generated 7 figure deals, 11 films from TIFF 2013 did the same. The difference is TIFF screens 2.5x as many films. Even eliminating the # of films with US distribution before TIFF started and cutting out foreign language films, producers were still twice as likely to get a seven figure deal at Sundance.

The Documentary King
TIFF is a much more diverse slate, but sorely lacking in docs. Roughly 1/3 of Sundance films are documentaries, while only about 1/10 of TIFF films are. Even then, docs were more likely to get distribution out of Sundance than TIFF and by a very wide margin. 90% vs 52%. The majority of docs that made the Oscar shortlist came from Sundance, as have a majority of nominees in the last five years.
Foreign Language Problem
In contrast to their #1 status as a place to launch documentaries, Sundance’s World Cinema lineup is far from a sure bet.
While only 41% of Sundance 2014 World Dramatic films have US distribution, that percentage is still higher than foreign language films that screened at TIFF. The % is higher even if we include all foreign language films and not just world or international premieres at TIFF. So even in Sundance’s weakest area your odds are still better than at TIFF.
That all noted, TIFF receives some high profile foreign language films that will ultimately generate bigger deals and make a dent in the US box office, but those are few and far between in an already very unprofitable arena.
So What Does a TIFF Screening Mean?
TIFF does two things that Sundance does not. It functions as a worldwide market and it is a frequent must for awards buzz films.
Sundance films do better on a domestic level. TIFF films are more likely to generate some form of worldwide interest and the majority of major worldwide players are in attendance.
Sundance has an international presence, but nothing on the same level of going into the Hyatt and taking the United Nations tour of film booths.
Sundance also doesn’t take studio films, which TIFF does. I would argue this is part of the problem TIFF films face. The competition for attention is so much higher with studio films in the mix that many simply get lost in the shuffle.
The DIY Mindset
In the age of DIY options at very low cost, one has to wonder why so many films at TIFF didn’t take advantage of Vimeo’s $10k offer in 2013. In fact, 55 world premieres still lack US distribution, which means with 100% certainty they turned down $10k to chase a pipe dream of success.The worldwide sales agent aspect at TIFF makes it a lot harder to discuss DIY options, but things are slowly starting to change.
This year was the first time multiple filmmakers were willing to openly discuss DIY options for release with me during the fest.
Sundance has their Artist Services program and some very notable DIY success stories (Detropia, Indie Game: The Movie, Upstream Color etc). But the biggest difference is Sundance is early in the year. There are tons of festivals left with which to build exposure going into release.
While it is almost always advisable to hit the festival circuit running, if one didn’t do that at Sundance, it’s easier to rev up the process than at TIFF when the year is nearly finished. If you don’t pursue additional festival screenings right away, your film would play TIFF and not screen anywhere until the following year. Remember there aren’t a lot of festivals in November/December. By that point people have moved onto Sundance and don’t even remember what they saw at TIFF.
The Take Away
Don’t buy into the hype about a festival without carefully looking at the info. While many Oscar winners have come from TIFF, the stats don’t lie. For domestic success, your odds are better with Sundance. This doesn’t make TIFF a bad festival, it’s easily the 2nd best launch pad in North America, but it’s important to know that your film is more likely to get a distribution deal out of Tribeca than TIFF if you have a documentary.
The consensus from this year’s TIFF was that there weren’t too many hidden gems, but with 288 features would any of us even know? At a certain point size is a liability and I think that TIFF needs to shrink its slate or get more creative when it comes to highlighting world premieres without big names.
Reminder: EVOLUTION OF A CRIMINAL & THE CIRCLE
The Spike Lee executive produced Evolution of a Criminal opens in NYC Friday October 10th at IFC Center. They are also crowdfunding to support their nationwide theatrical release. https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/948417025/evolution-of-a-criminal-theatrical-release
In partnership with Wolfe Releasing, TFC Direct will be theatrically releasing Switzerland’s Oscar entry, The Circle. It opens November 21st in NYC and will be expanding through beginning of 2015.
Bryan Glick October 9th, 2014
Posted In: Distribution, DIY, Film Festivals, Publicity
Tags: Bryan Glick, documentaries, film distribution, Film Festivals, film sales, international films, Sundance Film Festival, The Film Collaborative, Toronto International Film Festival
DCP failure rate is extraordinarily high. Should you make one?
In two prior posts, I chronicled how rapid technological change was impacting the exhibition side of independent film, and how this was affecting filmmakers and their post-production and delivery choices. In January 2013, in a post called “The Independent’s Guide to Film Exhibition and Delivery” I discussed the rise of the DCP in independent exhibition, and the potential dangers it posed to filmmakers on a budget. And later that year, I posted “Digital Tape is Dead” in which I gave further evidence that it was possible to resist the rise of DCP…at least for the time being… and the reasons for doing so.

photo credit: Bradley Fortner via photopin cc
It’s a little over a year later, so I am returning to the topic to take stock of what a difference another year makes. And as always, the main goal of this exercise is to help you, as filmmakers, to make the best post and delivery choices in finishing and exhibiting your films.
Of the many things that The Film Collaborative does, one of our core services is booking our clients’ and members’ films in public venues all over the world – including everything from film festivals, traditional theatrical venues, universities, art galleries, etc. Every year, this work hits a peak frenzy in October, which is unquestionably THE month of the year with the largest number of film festivals. By simply comparing our booking format totals from October 2013 to October 2014, I can see that once again the landscape of booking has evolved substantially in the last 12 months.
BOOKINGS IN OCTOBER 2013 (total 195 booking engagements):
BLURAY: 144
DVD: 25
DCP: 12
HDCAM: 10
Digibeta: 2
Quicktime File: 2
BOOKINGS IN OCTOBER 2014 (total 268 booking engagements)
BLURAY: 162
DCP: 84
DVD: 12
HDCAM: 6
Quicktime File: 4
Other than the fact that we are obviously a busy company (!), the main takeaway here is that the DCP’s slow and seemingly inevitable rise to the top is continuing, although the actual majority of venues (especially in the U.S.) are still trying to cut costs by the use of BluRay. In Europe, the DCP has already overtaken all other formats, and is nearly impossible to resist if you want to play in any reputable festivals or venues. And after DCP and BluRay, all other formats are now nearly dead worldwide, at least for now.
There are many reasons why this isn’t good news for independent filmmakers (which we’ll go into)…but the first and most obvious problem is that all of the filmmakers we work with are still making multiple HDCAMs! From the data above it is clear, STOP MAKING HDCAMS PEOPLE! I know many companies that have stopped producing them entirely, and are providing only on DCP, BluRay, and DVD.
Usually, an independent filmmaker’s first worry about DCPs is the initial price – indeed it is the most expensive exhibition format to make since the 35mm print. However, the good news is that it has already dropped in price quite a bit from 2013…now if you look around you are sure to be able to get an initial one made for $1,000 – $1,500 (compared to around $2,500 a year ago).
Now there is the really weird situation with the subsequent DCPs…and what you should pay to make additional copies. If you’ve seen DCPs, you’ll know that they often come in these elaborate and heavy “Pelican Cases” with a “Sled” hard drive with USB adaptors and power supplies. That’s the kind the studios use, and they will usually run you around $400 per additional DCP…which is expensive.
The strange thing is that every tech-savvy person I know tells me that this is all window-dressing, and that a regular “Office Depot style drive” USB 3 Drive for $100 serves exactly the same purpose and is actually a bit more reliable since it has less moving parts. Add to this the simple charge for copying the DCP (for which our lab charges only $50), and you’ve got subsequent DCPs at only $150 each…which of course is even cheaper than old tape-based formats like HDCAM and Digibeta.
If someone out there knows why one SHOULDN’T go with the more inexpensive option, I’m all ears. Call me, tweet us @filmcollab, leave a comment on our Facebook page! ‘Cause I haven’t heard it yet.
Of course, its still not a super-cheap $10 BluRay, but the truly annoying thing about the DCP and all its solid state technology and its fancy cases is that it is HEAVY, surpassing everything except old 35mm prints in weight. As a result, the cost of SHIPPING becomes a major issue for independents, and more than $100 every time you send since you obviously aren’t going to put your pristine file in regular mail. If you’ve been booking and playing films for a long time, you’ll know that $100 in shipping is often the difference between a profitable screening a not-so-profitable one…and so the cost adds up quickly.
It’s truly the cost of shipping that makes me sad that the BluRay is doomed as a major exhibition format. At one point, when filmmakers and distributors made “P&A” assessments for their films, the biggest cost in the “P” analysis was the cost of shipping heavy prints. For a brief and shining moment….from like mid 2013 to mid 2014… the lightweight BluRays took that part of the “P” out of the equation entirely…and that sure was nice.
But the (dirty and secret) truth is that COST isn’t the main problem with DCP. It is the RELIABILITY of the format. The horrible fact is that DCP is the most unreliable format in terms of playability that we have ever had….bar none that I can think of. BluRays used to have the reputation for failing often, but they were easy to include a back-up copy with, and they have drastically improved in the last two years such that they almost never fail. DCPs, however, now fail ALL THE TIME, at an alarming rate, and for an alarming number of reasons.
Rather than go into the deep tech-geek reason for DCP failures in venues all over the world…I am going to copy a few recent emails from labs, festivals, and venues I have been communicating with in the last couple of weeks. I promise you…all of this is just in the last two weeks! And all of these are all different films and different DCPs!
[EXAMPLE] On September 16th, XXXX wrote:
So, bad news guys, we couldn’t access the hard drive on this DCP, so it’s our thoughts that it is dead.
[EXAMPLE} On September 18th, XXXX wrote:
Nothing over here is recognizing this DCP. The drive appears to be EXT3 formatted and I think this may be why it’s not recognizing as a usable hard drive. Generally, we use NTFS and EXT2 formatted drives. This one does have a bluray backup, but if you can try to get us another DCP, that’d be cool.
[EXAMPLE} On September 17th, XXX wrote
We just got the DCP and the sled was loose and the final screw holding it came off. It’s the plastic thing that pops out. Just now I noticed that most of the screws on it are loose. It won’t play because I think we need to replace the screws?
[EXAMPLE} On September 22,, XXXX wrote
We are facing difficulties with the DCP as our Server does not seem to recognize the drive. We have spoken to your lab and we think it’s because our server cannot recognize Linux Files. We have about 100 DCPs in our festival, and this is happening to about 10 of our films. Can you offer any advice?
It is this last example that really cracks me up….if you happen to know anything about DCP you know that Linux was chosen as the best format for DCI-complaint files. So the fact that a festival could not read Linux, but could still read 90 out of 100 of their DCPs is absolutely mid-boggling, as I thought Linux was in fact the common denominator.
But I digress.
As filmmakers, is any of this what you want to be doing with your time? Do you really want to know about EXT3 and EXT2, and do you seriously want to worry about replacing loose screws on a drive? Do you want to reduce your whole filmmaking experience as to whether a venue can read Linux or not? Do you have time for this?
Just this weekend, we had a screening in North Hollywood where the sound on the DCP went out for the last 5 minutes of the film, all the way through the credits. Is this acceptable? I thought not.
It was better before. We don’t like to think that evolution is like this….getting worse rather than better….but in truth it often is. And this is one of those times.
The truth is, I will never trust this format. The DCP was created by a 7-member consortium of the major multinational studios called the Digital Cinema Initiative (DCI). It represented only the major studios…and created a format best suited to their needs. They have since adapted all the major venues to their needs. Is it any wonder that these needs do not represent the needs of independent filmmakers? Do we have any doubt that that any “consortium” would actively seek to suppress the needs of its competition? It created encryption codes only they can functionally work with. It put all the rest of us in danger, in my opinion. Let’s just talk about their unworkable encryption technology if we want to start somewhere. KDMs on independent films are a joke….leaving us more vulnerable to piracy than ever.
So, here is why the “P” matters more than ever. And why there is still GREAT reasons to hope. Just when you thought I was writing a depressing post, I am going to flip this b*itch. And I mean “b*itch” in the best manner possible.
The truth is…the age of cloud based computing, the no shipping, the no P in “P&A” reality is finally nearly upon us.
The truth is…it will not be long before we can use cloud-based services to deliver our films to venues all over the world. Of course, it is happening now….but it is not a mature system yet. But my guess is that it WILL be very soon. Definitely less than 5 years.
With all the new services like Google Drive, WeTransfer, DropBox, Vimeo, etc all rapidly evolving…..we are only months (if not years) from really delivering our films without help from middle men like Technicolor and FED EX. And that will be a good thing. A great thing really. I believe it will increase our indie profits many fold.
Already, every single day, I have numerous festivals asking me to DropBox them the films we are working with. In truth, I haven’t figured out really how to do that yet in quality levels I am comfortable with that also make financial sense. I am in constant dialogue with our lab and our tech people as to how to make this work in terms of uploading time, server space, and quality of presentation.
But it is clear to me that it IS happening over time….if anyone knows the secrets…again, I am ALL ears! Please call me! Because I truly believe that when we can remove the P from the P&A equation….and I mean truly remove it such that any number of prints and all shipping can be eliminated as easily as sending someone a link to an FTP or whatever…..we will re-enter an age where independent film distribution will make real financial sense. Imagine that, for a moment.
And the weirdest thing is I think it is truly happening… any day now.
NOTE: Step 4 in this blog series will be an analysis of how to deliver your film digitally and via The Cloud. We aren’t there yet….BUT that is what I will cover in the next post of this series. Hopefully new updates will happen by the end of the year!
Jeffrey Winter October 1st, 2014
Posted In: Digital Distribution, Distribution, DIY, Film Festivals, Theatrical
Tags: BluRays, DCP, DCP failure rate, Digital Cinema Package, DVD, film festival distribution, HDCam, Jeffrey Winter, Quicktime, The Film Collaborative, theatrical distribution
Is this mic on? Stop making these well worn filmmaking mistakes
I’m back to blogging after a long (2 years!) hiatus in law school and the first thing I want to discuss is something that frustrates us about the filmmaker consultations we give. At The Film Collaborative (TFC), it is shocking how much of what we said 5 years ago when we first started the company and what we continue to say over and over again has not trickled down and stuck to filmmakers.
While we like to think that we are changing minds and getting filmmakers to be more proactive about making their own decisions regarding distribution of their films, sadly, this doesn’t seem to be the case in the majority. The same issues keep coming up (no you probably won’t be getting a 7 figure deal for distribution…no your film is not a fit for Sundance…no you shouldn’t just sign any deal that slides across the table).
Maybe you’re afraid of letting go of the notion that your job is only to make a good film and someone will buy it for big sums and you can move on fast to your next film.
Maybe you’re worried that if you cannot look an investor in the eye and say that the odds of selling and making all the film’s money back within a year or two are good, you won’t be able to make films.
Maybe you aren’t actually following any of the information currently coming out of every festival panel and industry publication about how the distribution world stands today.
But that doesn’t mean new information isn’t available and the independent film world still works like it did in 2008.
This is information we analyze daily at TFC. Clinging to the old mythology just makes it easier for distributors to cling to non-transparency in how money is made in distribution and it’s all a vicious and unsustainable cycle. You need to know the real story on how deals are structured now, what kinds of revenue is being recouped and why, and what role audience data plays in the continuation of your filmmaking career. This is not some 90’s pipe dream of make a film, reap immediate millions.
In law, they call that “willful blindness” where a person seeks to avoid liability for a wrongful act by intentionally putting his or herself in a position where he or she will be unaware of facts that would render him or her liable. It’s not pretty to see, especially after all this time of talking about properly laying ground-work for self financed distribution. It has to stop and it will eventually because someone who is willfully blind won’t be working as a filmmaker for much longer.
Of course it’s not all about money, it’s also about building your audience and having your film seen and developing your career. These are actually all quite connected, much more often than not.
Here’s a list of things we have been saying for years and keep saying. Please let this stuff stick, it’s good for you! And the more people practice it, the healthier this will be for artists and for the business in general.
Top 15 mistakes made by filmmakers that shouldn’t keep happening are:
Making a horror film and only start thinking in August about how to release it by October of the same year. If you are planning a digital release, you need about a 4-6 month lead time.
Not building community around your film until after you premiered it at a festival (or worse, completed the circuit) such that then you squandered opportunities to build buzz, demonstrate and test audience appeal, and build awareness and marketing or organizational partnerships for future release before your buzz is gone.
Not clearing music rights believing that your distributor will be happy to pay for clearance. Profit margins are already slim for distributors, so they aren’t going to outlay for this expense. Plus, it makes you look unprofessional and extremely misinformed if you don’t have all of your clearances. Plan to work with a music supervisor.
Stealing money from your marketing and distribution budget to feed your production budget even though both are needed. In fact, if you can’t market and distribute your film, you probably shouldn’t even make it. Stop with assuming you won’t need to market and distribute your film. You will at least need to build up some kind of audience awareness and it will be smart for you to start getting immediate revenue from direct distribution.
Making your first documentary largely out of stock footage, which is probably the most expensive kind of documentary you can make. Stock footage is expensive to clear and if you have no track record of success in filmmaking, it is better to steer clear of making an expensive film as your first attempt.
Making a film with no notable names, no clearly identifiable audience, and no plan for how to distribute or market the title. This is an especially bad idea if you were planning to have someone else buy it and distribute it because it has virtually no market value.
Relying on box office gross as an indicator of the commercial success of a film, and using those numbers for the business plan of your film. Box office revenue is only top line revenue, not net revenue and certainly not an indicator of profit.
Believing that MGs in the 6-7 figure range are common for films without A-list talent. Read the trades after a major festival or film market and see what MGs are paid and for what level of talent in the film. If you don’t have this level, you aren’t getting that MG.
Skipping taking good photography on set and thinking frame grabs of the cast and crew will cut it when formulating key art and meeting deliverable requirements from buyers. Here is our post on what is needed for making key art. Still images are absolutely imperative to film sales and film promotion, but also to populate social media channels. Don’t skimp on photography.
Having a 4-minute trailer. Really? Please don’t. Also related, letting your intern or the editor of your film cut your trailer. Please hire a professional trailer editor because it is that important to gaining audience interest in seeing your film.
Forgetting that artwork on digital platforms is small, not theatrical poster size. It demands clear imagery with no extra text (laurels, URLs, credit block, rating etc).
Conflating “distributor” with “aggregator” and even with “platform” – they are different, the deals will be different, your expectations should be different, etc. This leads filmmakers to make bad or incomplete decisions. See our post on distribution terms.
Many filmmakers drastically “overthink” their festival strategy, and hold back from festival invitations for fear that actions taken now will overexpose the film and hurt its chances with press and distributors later. The truth is that INACTION is the far greater danger. By all means, you should obsess about the right world and international premieres …after that, just identify the best festival opportunities in each local market and let it fly, making sure to also address the festivals that cater to your niche along the way.
Hiring a lawyer who does not know the film business to handle your film deals. Okay, that’s a shameless plug since I’m an attorney now. But truly, as much as knowing the law matters, knowledge of what can be negotiated in a film distribution deal matters so much when it comes to monetizing rights and protecting your work.
Conducting screenings of your film (test screening as well as festivals) and not having a system for collecting email contact details so you can keep in touch about the progression of the release. When will you have another chance to contact these people again? Maximize your ability to keep in contact. There are now some text to subscribe services you can use rather than pass the clipboard.
A lot of film consultants, industry bloggers, film festival panelists, and others all saying the same thing so it’s time to realize what they are telling you is true. Can you hear me? Is this mic still on? It’s time not just to hear, but to listen and follow the advice people are freely telling you. You should no longer continue to make these mistakes.
Wishing you all the good things in your filmmaking career.
Orly
Orly Ravid September 24th, 2014
Posted In: Distribution, DIY, Film Festivals, Marketing
Tags: biggest mistakes filmmakers make, film distribution, film marketing, independent film, mistakes filmmakers should avoid, Orly Ravid, The Film Collaborative
ERROR_image_1.jpg)
error_image_2.jpg)